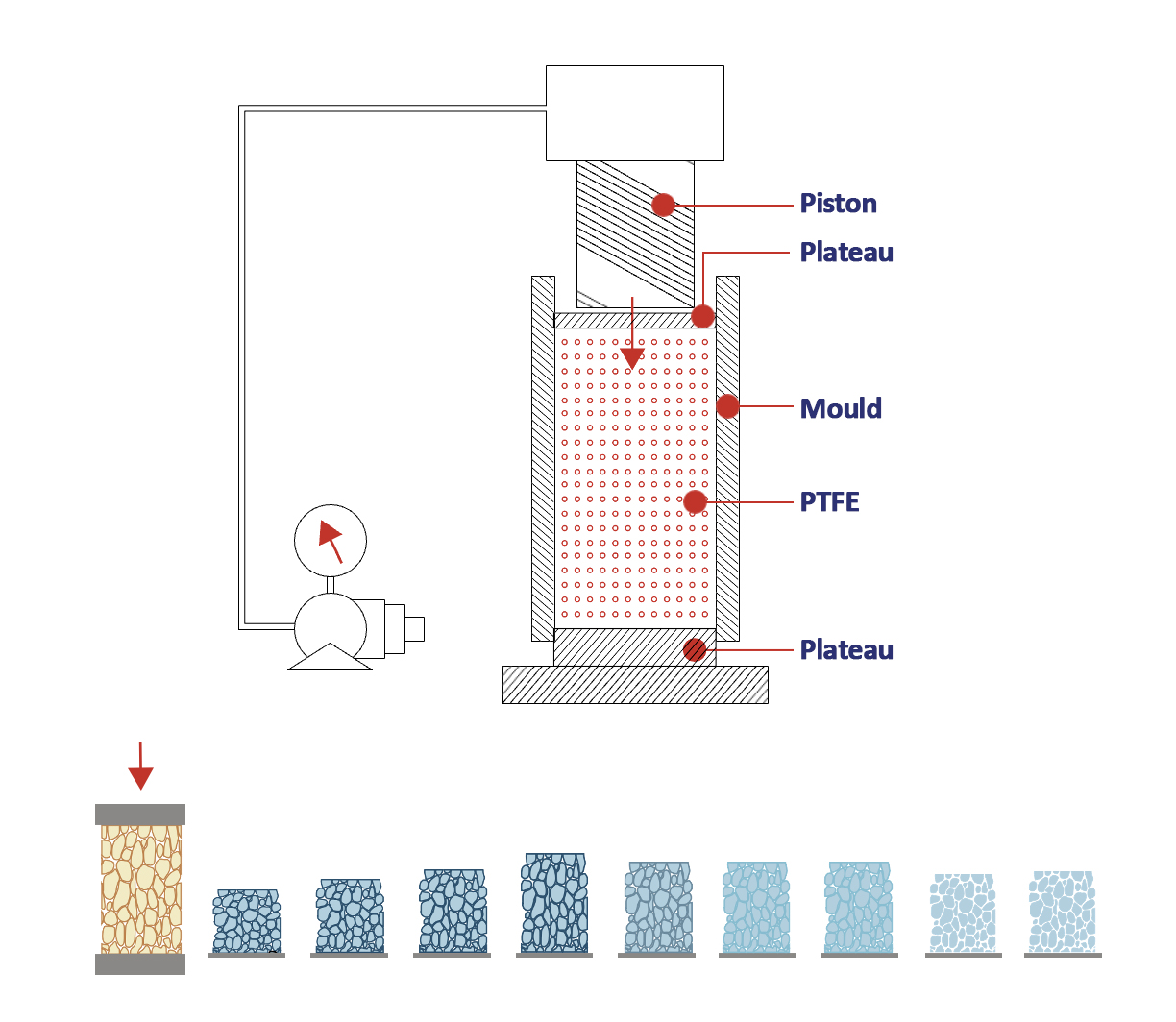
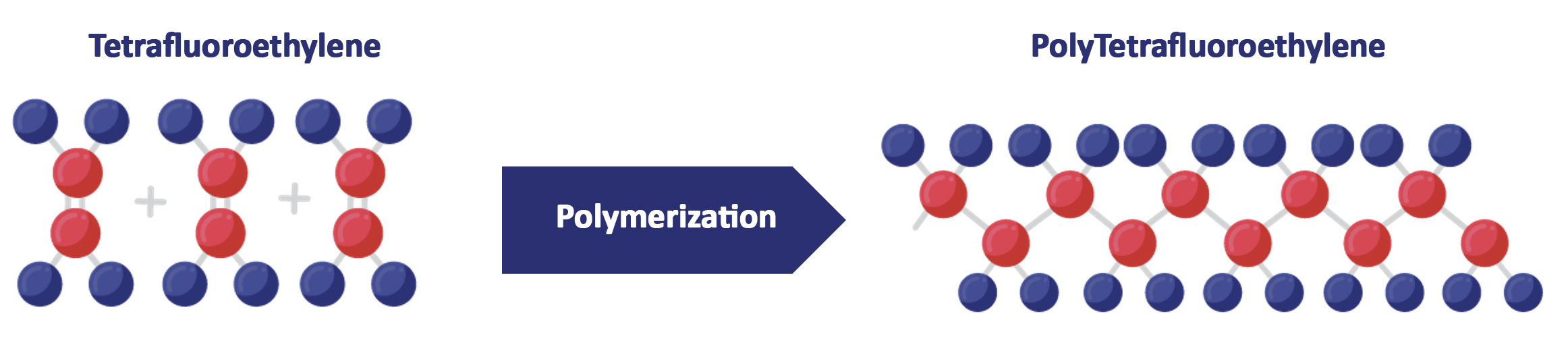
What is Teflon® (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a polymer known worldwide as Teflon® – registered trademark of Chemours® – has remarkable chemical, electrical, mechanical, thermal and physical properties, having a non-stick characteristic (“ice over ice”) and, therefore, can be used in different segments and applications in which these characteristics are necessary.
Features
Among its main characteristics we can mention its properties:
Compounds
Some properties can be improved by adding fillers. Typical additives include fiberglass, graphite, bronze and molybdenum disulfide.
Characteristics of adding loads:
• Abrasion resistance;
• Compressive strength;
• Dimensional stability;
• Thermal stability;
• Electrical conductivity.
Main Properties/Constitution
The chemical bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the most resistant in all organic chemistry.

| Compound | %Weight | Positive Effect | Negative Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) |
Up to 5% combined with bronze and fiberglass | Improves sliding properties | It is no longer non-toxic |
| Increases wear resistance | Absorbs moisture | ||
| Graphite | Up to 25% combined with fiberglass, bronze and carbon | Improves sliding properties | It is no longer non-toxic |
| Reduces the coefficient of friction | Absorbs more moisture | ||
| Improves thermal conductivity | Loss of electrical insulation | ||
| Carbon | Up to 35% combined with graphite, bronze and fiberglass | Increases compressive strength | |
| Increases hardness | |||
| Increases wear resistance | It is no longer non-toxic | ||
| Improves thermal conductivity | Absorbs moisture | ||
| Electrically conductive | Loss of electrical insulation | ||
| Resistant to hydrofluoric acid | |||
| Bronze | Up to 60% combined with MoS2 | Increases compressive strength | It is no longer non-toxic |
| Increases hardness | Increase in project weight | ||
| Increases wear resistance | Unsatisfactory for some acids | ||
| Reduces cold flow | Reduces tensile strength | ||
| Improves thermal conductivity | Loss of electrical insulation | ||
| Fiberglass | Up to 25% combined with graphite and MoS2 disulfide | Increases stiffness | It is no longer non-toxic |
| Increases wear resistance | Reduces slippage | ||
| Reduces cold flow | Absorbs moisture | ||
| Increases compressive strength | Increases the coefficient of friction | ||
| Resistance to organic solvents | Unsatisfactory for some acids |

